The 2008 Crisis and the Rise of Bitcoin: How Blockchain Technology Can Protect Us
As the 2008 financial crisis evolved, American families watched in horror as the government bailed out Wall Street bankers who had caused the crisis with their reckless and greedy actions. While the bankers were bailed out and protected, ordinary citizens were left vulnerable and lost.
The crisis exposed the lawlessness of the traditional financial system. This led many individuals to question the stability and transparency of the financial system. In the aftermath of the crisis, there was a growing demand for alternative financial solutions that deliver more transparent, secure, and decentralized solutions. This is what Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies provide.
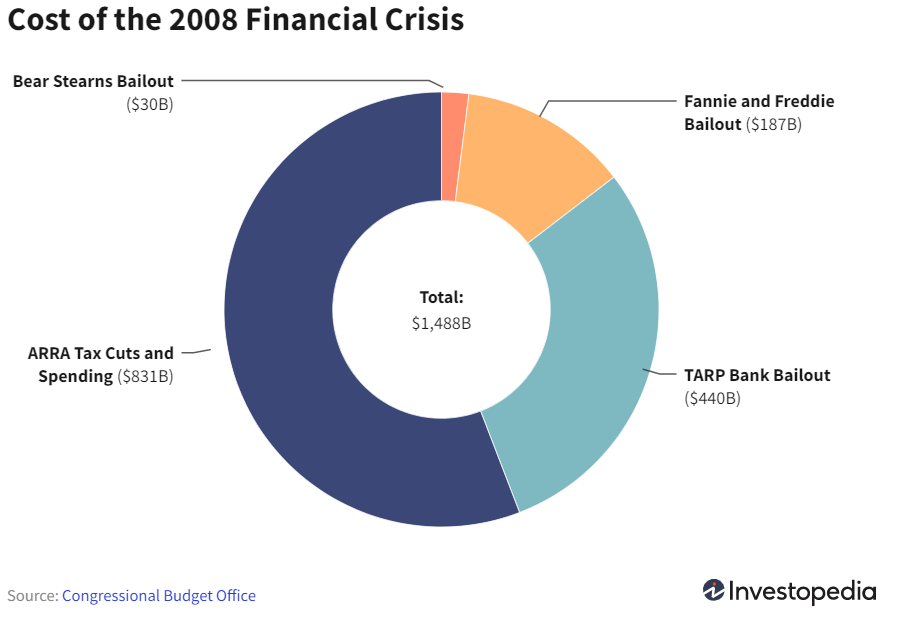
2008 Financial Crisis: A look at the Numbers
- 8.8 million jobs lost
- Unemployment spiked to 10% by October 2009.
- 8 million home foreclosures.
- $19.2 trillion in household wealth evaporated.
- Home price declines of 40% on average—even steeper in some cities.
- S&P 500 declined 38.5% in 2008.
- $7.4 trillion in stock wealth lost from 2008-09, or $66,200 per household on average
- Employer-sponsored savings/retirement account balances declined 25% or more in 2008.
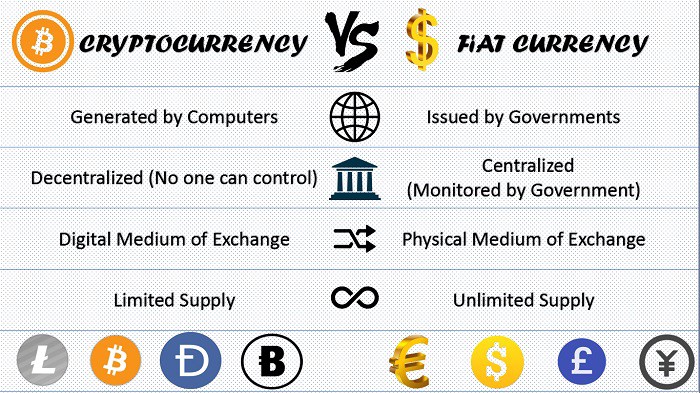
Bitcoin: A Decentralized Digital Currency
The 2008 financial crisis was a major catalyst for the development of Bitcoin. The Bitcoin Whitepaper was published on October 31st, 2008 by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. The Bitcoin Whitepaper laid out the foundation for a decentralized digital currency.
At its core, Bitcoin is based on the principles of decentralization and individual sovereignty.
- Although the Bitcoin Whitepaper was published in 2008, it's worth knowing that Bitcoin alone wasn't invented in 2008. Since the early 90s, many researchers, cryptographers, and programmers have been talking about how to use cryptographic methods to create a decentralized digital currency. Nevertheless, it was not until the publication of the Bitcoin Whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 that a recognized approach for a decentralized digital currency was realized.
The Decentralized, Peer-to-Peer System Proposed in the Bitcoin Whitepaper
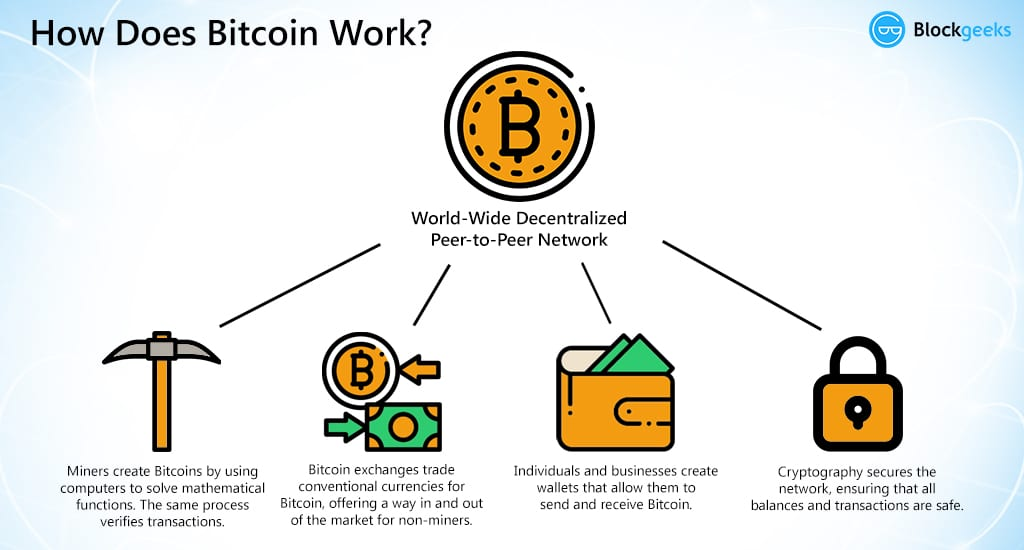
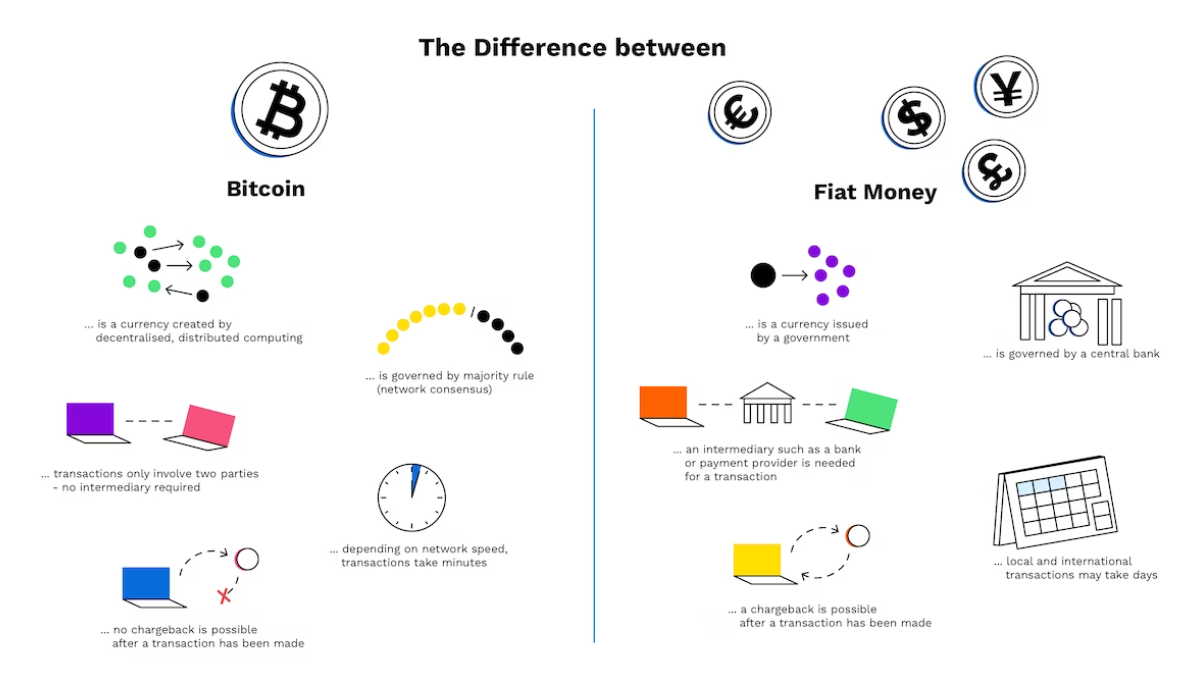
In the Whitepaper, Satoshi proposed a decentralized, peer-to-peer system for conducting electronic transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. The system would be secured by cryptography and powered by a grid of users that contribute their computing power to process transactions.
The Innovation of the Blockchain and Its Impact on Security and Decentralization
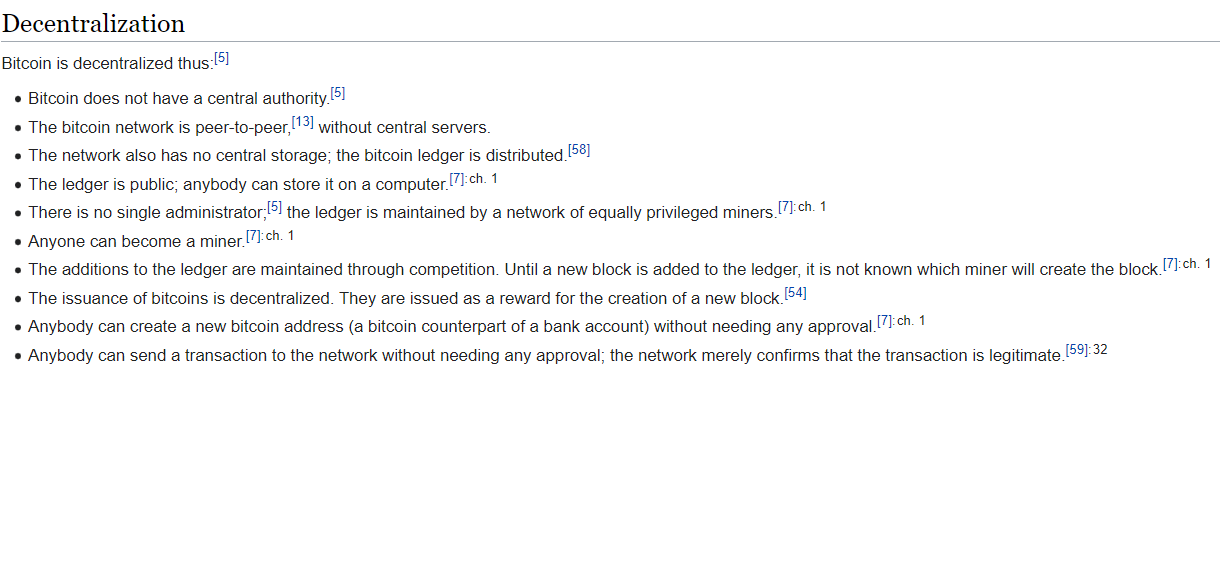
One of the major innovations of Bitcoin is the use of a decentralized ledger, known as the blockchain, to record and verify transactions. The blockchain is a distributed database that is maintained by a network of users, that spans all across the world. This makes it impossible for any entity to prevent or intercept transactions.
The Fixed Maximum Supply of Bitcoin and Its Impact on Inflation and Stability
In the case of Bitcoin, the issuance rules are detailed in the Bitcoin Whitepaper. The supply of new Bitcoins is tied to the mining process. In this process, users contribute their computing power to settle transactions. As a reward for processing transactions on the Bitcoin network, miners are rewarded with a fixed amount of Bitcoins. This is how the Bitcoin network will operate until 21 million coins are issued, which is the maximum supply.
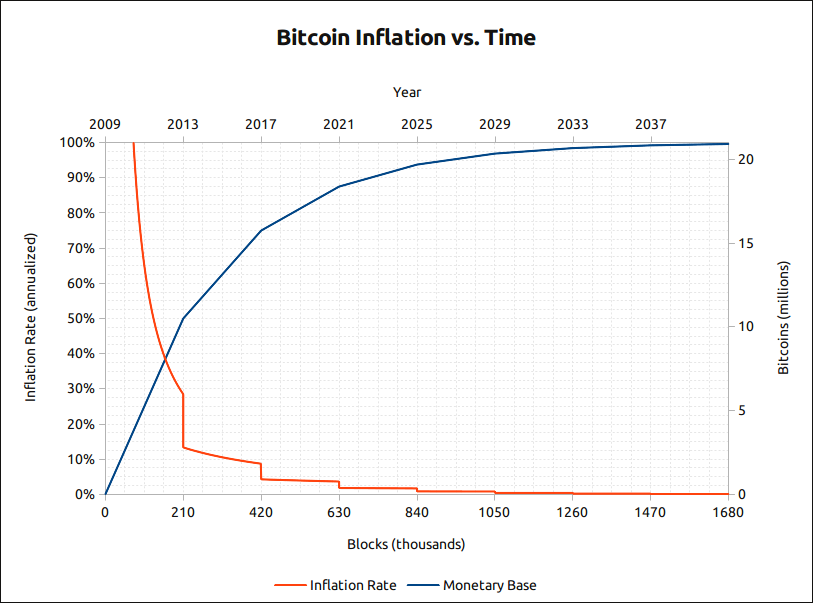
Bitcoin is designed to ensure the value of its currency is not corrupted over time through inflation. By limiting the number of Bitcoins that will ever be created, the significance of Bitcoin is expected to remain fruitful.
Unlike fiat currencies, which are distributed on a whim by bureaucratic controls, the supply of Bitcoin is fixed. It can't be inflated beyond 21 million. This means that the value of Bitcoin is not subject to the same inflationary forces as fiat currencies.
Preventing the Next Crisis: How Bitcoin and Blockchain Could Help
Decentralization:
One of the different benefits of Bitcoin and blockchain technology is that it is decentralized. This means that it is not controlled by a single person or authority. This decentralization decreases the risk associated with economic crises triggered by the failure of a single large institution. This is because no one can seize control of a decentralized system like Bitcoin.
Transparency:
The lack of transparency in the financial system was one of the major factors that contributed to the 2008 economic crisis. Trusted credit agencies mislead investors by giving AAA ratings to risky mortgage-backed securities. In reality, many of these securities were backed by dangerous mortgages that were likely to default, leading to widespread losses when the housing market crashed.
In contrast, Bitcoin's decentralized ledger, known as the blockchain, provides a transparent and immutable record of all transactions. This means that users can trust that their transactions are accurately recorded and that their money is safe and secure. Additionally, the blockchain is secured by cryptography, which makes it nearly impossible for any single entity to manipulate or censor transactions.
The use of blockchain technology could also help to increase trust in the financial system, as it provides a secure and tamper-proof record of transactions. In a traditional financial system, trust is often based on the reputation of central authorities like banks or credit agencies.
The decentralized public ledger that underlies Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, is a public and transparent record associated with every transaction. The open and transparent nature of the blockchain could have exposed risky financial practices, fraud, and other forms of financial misconduct before the crisis. This could have prevented the crisis and led to more accountability.

Removing Intermediaries:
Bitcoin removes the need for middlemen like banks and credit agencies Instead, Bitcoin users can directly send and receive payments from one another. This not only reduces the cost of processing transactions but also increases the speed and efficiency of the financial system.
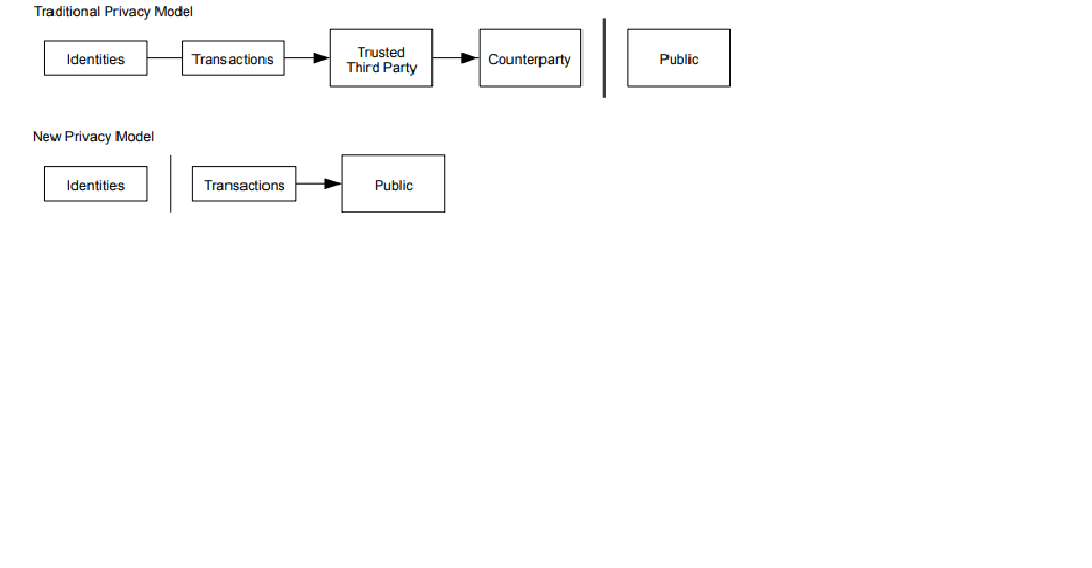
One of the major benefits of this is that it eliminates the need for users to trust a central authority. In the traditional financial system, users must trust banks and credit agencies to hold, manage, and record their money. However, as we learned in 2008, these centralized authorities are not always transparent or accountable. They can be prone to mistakes, fraud, and corruption.
Equal access to financial services:
One of the elements that contributed to the 2008 financial crisis was the concentration of financial power in the hands of a few large financial institutions. These institutions had significant influence over the financial system and were able to make decisions that had widespread consequences around the world.

In a decentralized financial system powered by Bitcoin and blockchain technology, access to financial services is equal. Individuals can transact directly with one another without the need for intermediaries like banks. This could reduce the concentration of power in the financial system and prevent the kind of systemic failure that occurred in 2008.
Additionally, the use of blockchain technology could allow individuals in under-banked or unbanked regions to access financial services that were previously out of reach. By providing equal access to financial services, Bitcoin and blockchain technology could help to create a more stable and inclusive financial system.
Protection Against Government Interference Through Decentralized Governance
With Bitcoin and blockchain, the financial system would be less vulnerable to interference from governments and central authorities, reducing the risk of a crisis caused by their poor policy decisions. Decentralized governance on a blockchain allows for a better democratic process in economic decision-making, potentially preventing risky practices from being enforced.
Conclusion:
The 2008 financial crisis was a devastating event that had far-reaching consequences. Risky financial creations, loose lending standards, and a lack of transparency in the financial system all led to the economic disaster that is still being felt today. The crisis exposed the vulnerabilities of this system and sparked a demand for more transparent, secure, and decentralized options.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have since gained significant recognition as a viable alternative, with many people using them for online payments, cross-border transactions, and as a store of value.
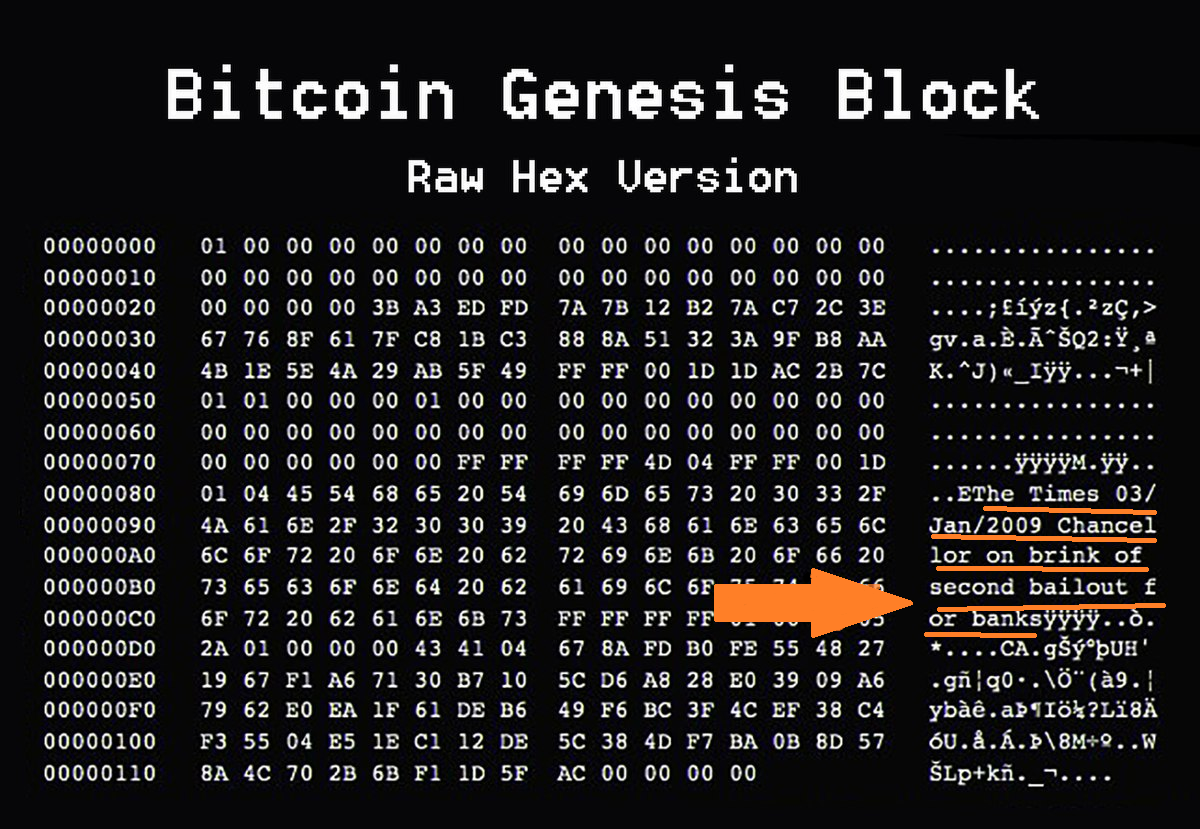
Overall, the idea behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies has the potential to change multiple industries and have a lasting impact on the way we think about money and the role of banks in the economy.
While it is impossible to say for sure what the future will hold, it is clear that Bitcoin and blockchain technology has the potential to mitigate the impact of future financial crises. By providing a decentralized, transparent, and secure platform for conducting financial transactions, Bitcoin and blockchain technology could prevent the same type of systemic collapse that we saw in 2008.